This Electricity-Free Cooler Developed By IIT Researchers Can Replace Air Conditioners! How It Work?
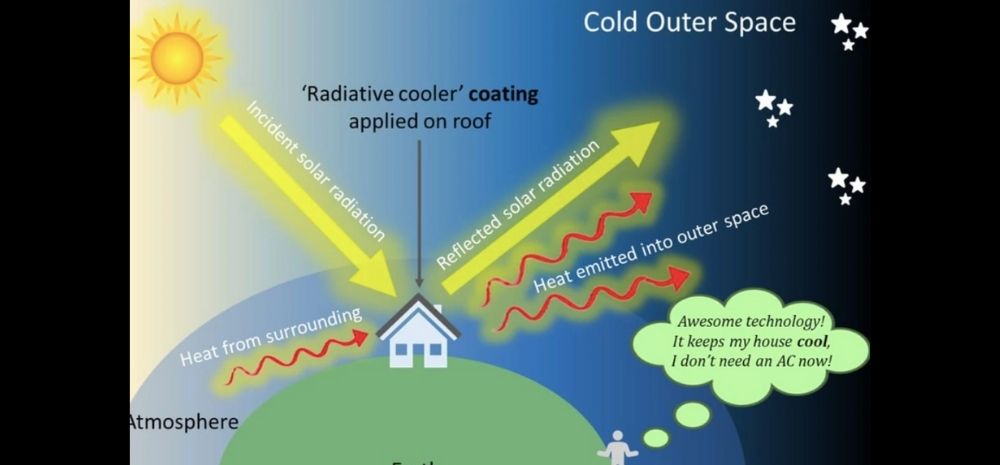
Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati researchers have built a ‘Radiative Cooler’ which does not require electricity to operate.
This is an affordable and efficient ‘passive’ radiative cooling system that can serve as an alternative to ACs.
The coating material is an electricity-free cooling system that can be applied in the rooftops and functions during both day and night.
Contents
What makes this special?
Till date, passive radiative coolers have not been able to provide sufficient cooling during daytime.
Therefore, researchers at IIT Guwahati set out to resolve these issues and developed an affordable and more efficient radiative cooling system that can operate during the day as well as night.
How it works
These coolers operate by emitting the heat absorbed from the surroundings in the form of infrared radiations which can pass through the atmosphere before being released into the cold outer space.
Most passive radiative coolers were able to operate only at night so far.
But this one can operate during the day by reflecting solar radiation.
Why is it challenging to build one that works in sunlight?
Professor Debabrata Sikdar said that this endeavor is more challenging due to the simultaneous requirement of high reflectance in the entire solar spectral regime and high emissivity in the atmospheric transmittance window.
The solar spectral regime ranges from 0.3 to 2.5 micrometre wavelengths.
Solar spectrum consists of radio waves, microwaves, visible light, ultraviolet rays, X-rays and gamma rays.
Meanwhile, the atmospheric transmittance window ranges from eight to 13 micrometre wavelengths.
Atmospheric transmission is the process by which radiation is propagated through a medium.
Atmospheric transmittance is the ratio of the transmitted radiation to the total radiation incident upon the medium.
As an alternatives To ACs
It works as a proper alternative to conventional air conditioning systems since it requires no external sources for their operations.
Traditional cooling technologies dump the waste into the surroundings.
But radiative cooling involves a unique process which cools an object on Earth by sending excessive heat directly into the extremely cold universe.
How daytime cooling is achieved
This is achieved using polymer-based passive radiative coolers.
However, oxidation degrades the polymers resulting in a limited lifespan.
This issue has been addressed using thin films of silicon dioxide and aluminum nitride, which have low optical density corresponding to the wavelength range of solar and atmospheric radiations.
The radiative cooler designed by the researchers at IIT Guwahati achieved 97 per cent reflectance for solar and atmospheric radiations and 80 per cent emissivity for radiations in atmospheric transmittance wavelengths
Net cooling power is estimated to be 115 Watts per metre square which could reduce ambient temperatures up to 15 degrees below the outside temperature.
Key advantages
The design is lithography-free and large-area compatible.
Lithography is a printing process that involves using a stone or metal block on which an image has been drawn with a thick substance that attracts ink.
The design ensures effective cooling during daytime without any need to adjust the angle or position or the cooler towards the Sun.
The radiative cooler provides around 1.6 times more cooling power compared to a recent cooler design which achieves a comparable reduction in ambient temperatures.

Comments are closed, but trackbacks and pingbacks are open.